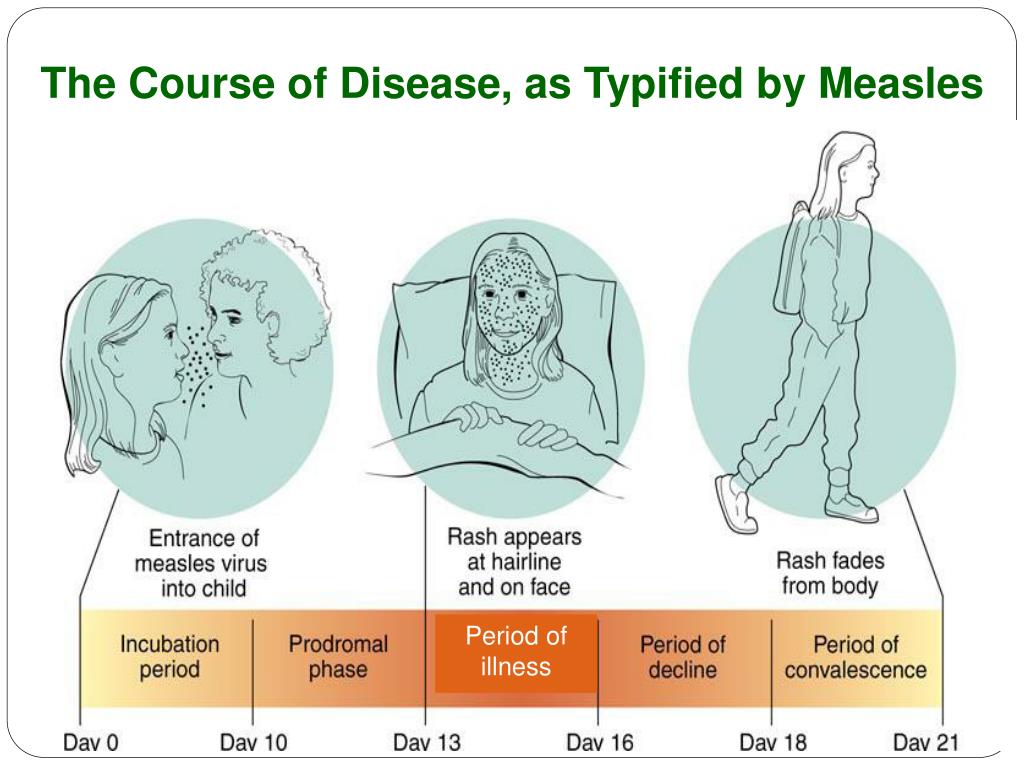
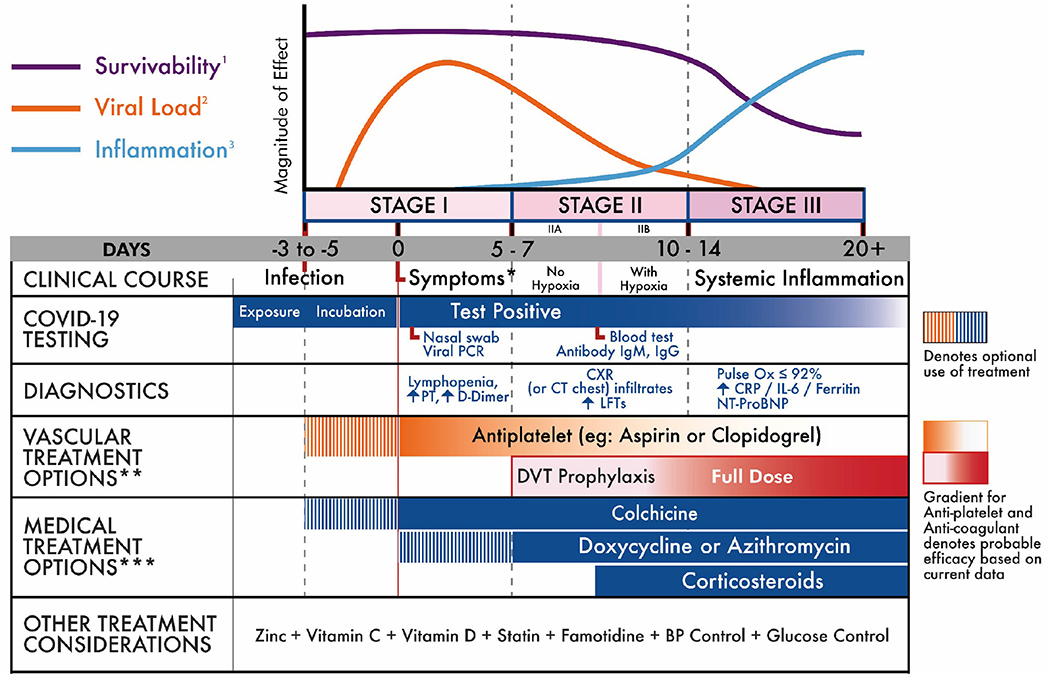
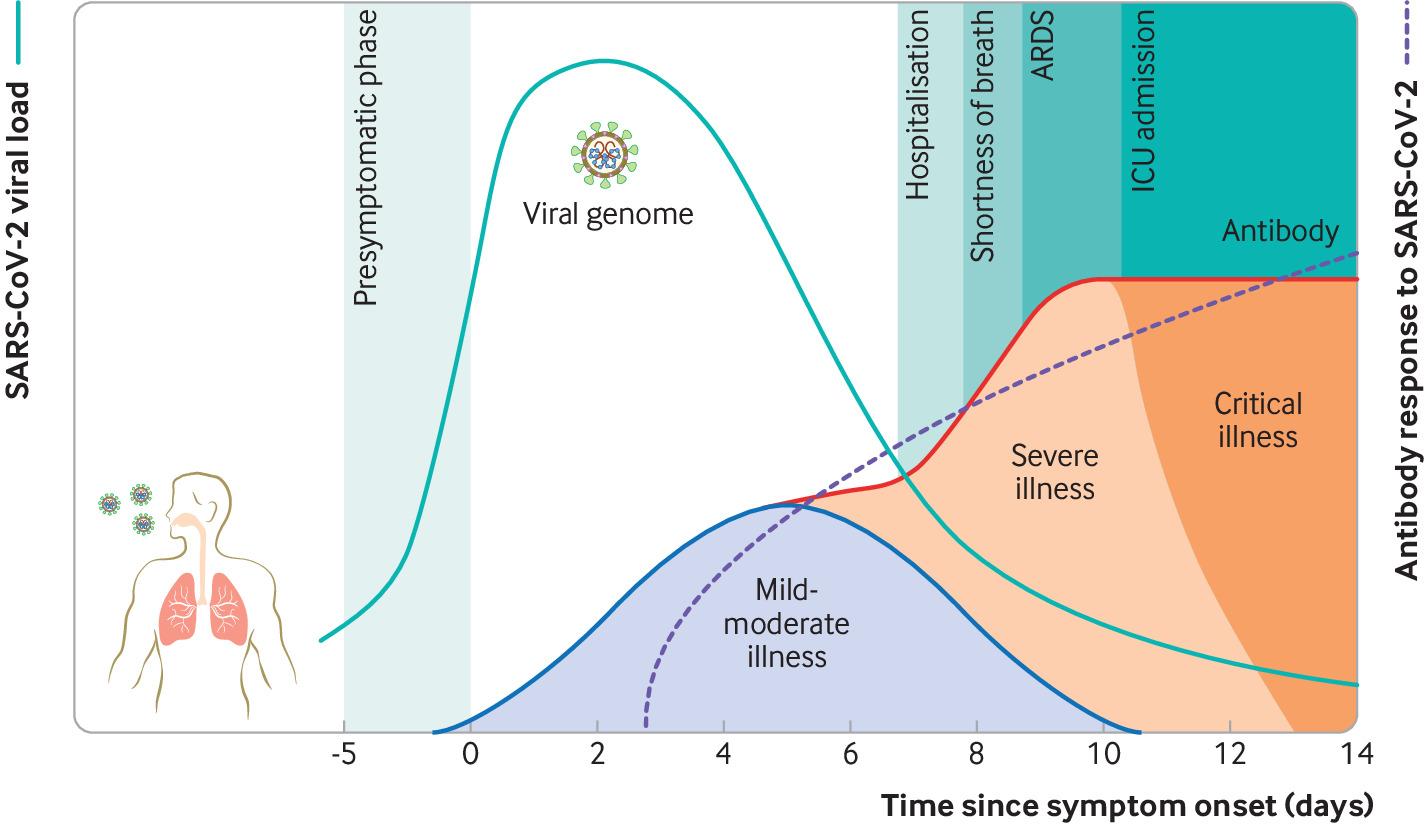
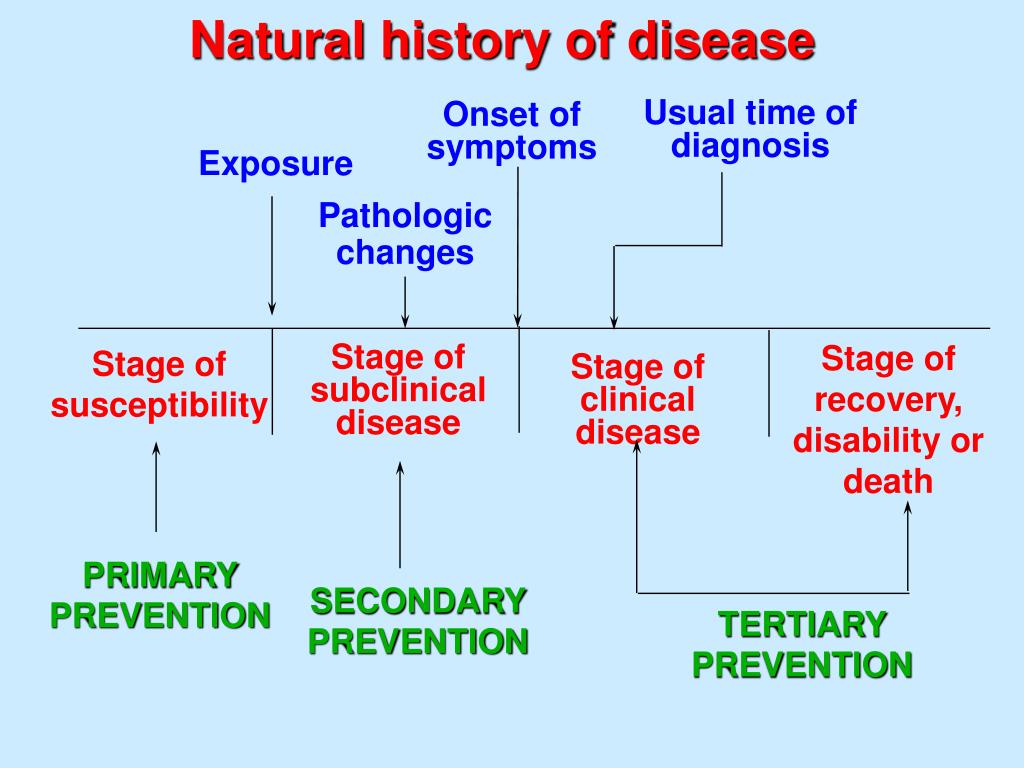
Course Of Disease
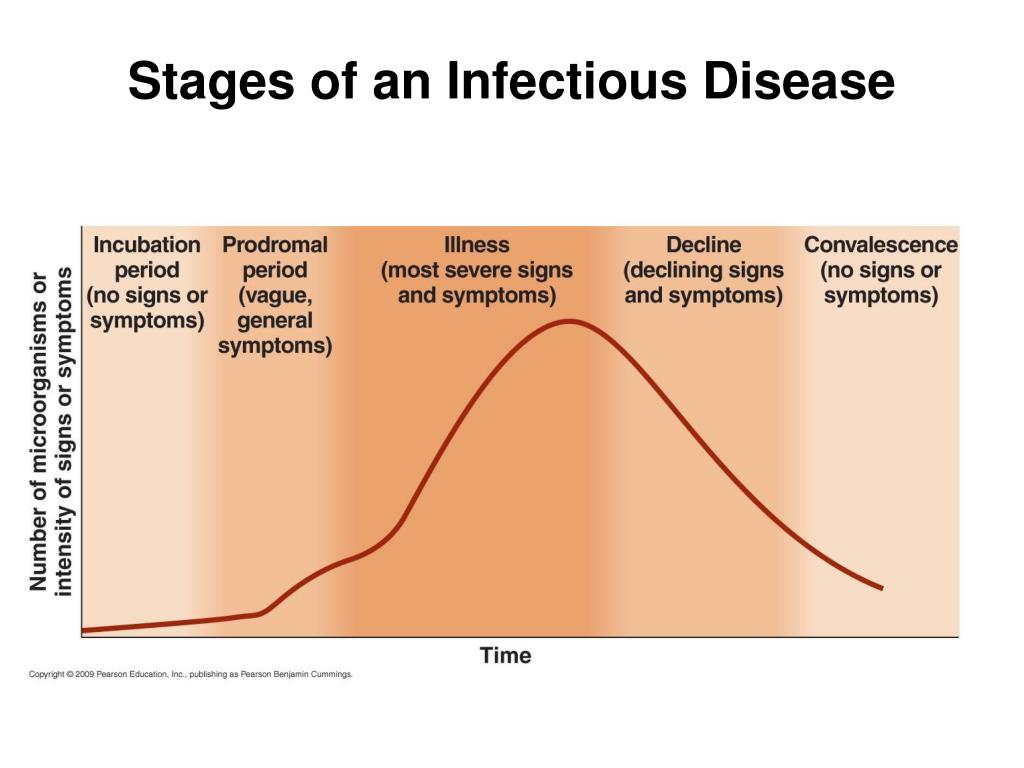
Course Of Disease - Disease can result in a temporary or. Patients want to know what the future holds for a broad range of conditions and the outcomes. These terms can be used interchangeably. Most diagnoses are made during the stage of clinical disease. Disease course is the progression of a disease over time and is a key factor in determining an individual’s prognosis. What causes illnesses to arise and spread, and how can we treat and prevent them? [4] typical courses of diseases include: Prognosis, defined as the likely course of a disease or illness, encompasses far more than this. Disease can result in a temporary or. The 'course of disease' refers to the progression and development of a medical condition over time, including factors influencing its trajectory, such as etiological and risk factors, social. The course of a disease, also called its natural history, [3] is the development of the disease in a patient, including the sequence and speed of the stages and forms they take. What causes illnesses to arise and spread, and how can we treat and prevent them? The natural history of a disease is also referred to as the course of the disease, or its development and progression; Most diagnoses are made during the stage of clinical disease. Disease can result in a temporary or. Delay in recognition or undertreatment may. If you’re curious about the mysteries of disease, you can expand your medical knowledge and career. A disease is expected to follow a particular series of events in its development (pathogenesis), and to follow a particular clinical course (natural history). Here, we review the progress that has been made in predicting the future for any given patient with inflammatory bowel disease—whether that is the course of disease that they. Disease course refers to the progression of a disease over time, including aspects such as disease trajectory, life expectancy, and the terminal nature of the disease. A disease is expected to follow a particular series of events in its development (pathogenesis), and to follow a particular clinical course (natural history). Most diagnoses are made during the stage of clinical disease. [4] typical courses of diseases include: The natural history of a disease is also referred to as the course of the disease, or its development and. Disease course refers to the progression of a disease over time, including aspects such as disease trajectory, life expectancy, and the terminal nature of the disease. The course of a disease, also called its natural history, [3] is the development of the disease in a patient, including the sequence and speed of the stages and forms they take. Patients want. Monocyclic, polycyclic (flares of disease while off treatment), or chronic continuous disease. [4] typical courses of diseases include: If you’re curious about the mysteries of disease, you can expand your medical knowledge and career. A disease is expected to follow a particular series of events in its development (pathogenesis), and to follow a particular clinical course (natural history). Disease can. A disease’s course is a combination of the particular disease, the. In today’s world, where infectious diseases are a constant threat, it is crucial to understand the stages of infection in order to effectively diagnose and treat them. Infection occurs when an organism,. A disease is expected to follow a particular series of events in its development (pathogenesis), and to. In some people, however, the disease process may never progress to clinically apparent illness. Disease can result in a temporary or. The process of a pathological condition from inception to resolution. Disease course refers to the progression of a disease over time, including aspects such as disease trajectory, life expectancy, and the terminal nature of the disease. Here, we review. The ability to predict the course of disease and the effect of interventions is critical to effective medical practice and health care management. Most diagnoses are made during the stage of clinical disease. These terms can be used interchangeably. The course of a disease, also called its natural history, [3] is the development of the disease in a patient, including. Prognosis, defined as the likely course of a disease or illness, encompasses far more than this. Patients may follow one of three disease courses: A disease’s course is a combination of the particular disease, the. There are five stages of infection, each with a different duration and symptoms. The process of a pathological condition from inception to resolution. Here, we review the progress that has been made in predicting the future for any given patient with inflammatory bowel disease—whether that is the course of disease that they will. There are five stages of infection, each with a different duration and symptoms. Disease can result in a temporary or. A disease is expected to follow a particular series of. Psychology definition of disease course: There are five stages of infection, each with a different duration and symptoms. These differences also depend on the type of infection. If you’re curious about the mysteries of disease, you can expand your medical knowledge and career. Patients may follow one of three disease courses: Monocyclic, polycyclic (flares of disease while off treatment), or chronic continuous disease. In today’s world, where infectious diseases are a constant threat, it is crucial to understand the stages of infection in order to effectively diagnose and treat them. If you’re curious about the mysteries of disease, you can expand your medical knowledge and career. Patients want to know what. [4] typical courses of diseases include: Infection occurs when an organism,. A disease’s course is a combination of the particular disease, the. These terms can be used interchangeably. Disease course refers to the progression of a disease over time, including aspects such as disease trajectory, life expectancy, and the terminal nature of the disease. Disease can result in a temporary or. What causes illnesses to arise and spread, and how can we treat and prevent them? A disease is expected to follow a particular series of events in its development (pathogenesis), and to follow a particular clinical course (natural history). Patients may follow one of three disease courses: The ability to predict the course of disease and the effect of interventions is critical to effective medical practice and health care management. The course of a disease, also called its natural history, [3] is the development of the disease in a patient, including the sequence and speed of the stages and forms they take. These differences also depend on the type of infection. The 'course of disease' refers to the progression and development of a medical condition over time, including factors influencing its trajectory, such as etiological and risk factors, social. Disease course is the progression of a disease over time and is a key factor in determining an individual’s prognosis. Most diagnoses are made during the stage of clinical disease. Delay in recognition or undertreatment may.PPT Descriptive Epidemiology of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) PowerPoint
PPT INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGY PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Ch 14 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology PowerPoint
Frontiers Current Understanding of COVID19 Clinical Course and
PPT Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases PowerPoint Presentation, free
Every Picture Tells a Story The Disease Course of COVID19 American
Disease Stages Figure 14.5 Diagram Quizlet
The 5 stages of disease and prevention
PPT History of Epidemiology PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Stages Of Infectious Disease
Prognosis, Defined As The Likely Course Of A Disease Or Illness, Encompasses Far More Than This.
If You’re Curious About The Mysteries Of Disease, You Can Expand Your Medical Knowledge And Career.
The Process Of A Pathological Condition From Inception To Resolution.
Disease Can Result In A Temporary Or.
Related Post: