Crash Course Biological Molecules
Crash Course Biological Molecules - In this episode of crash course, hank introduces you to the complex history and terminology of anatomy & physiology. This material focuses on the critical roles of the four classes of organic molecules essential for life: Share free summaries, lecture notes, exam prep and more!! 1) essential sources of energy, 2) energy storage, 3) instructions to your body why do lipids group together? What are the four biological molecules? Click to see the original works with their full license. You are what you eat crash course biology #3 1. Biology is the scientific study of living organisms and their interactions with the environment. Valine protects and builds muscle tissue. List two specific amino acids and briefly identify their main roles in the body. Biology is the scientific study of living organisms and their interactions with the environment. List two specific amino acids and briefly identify their main roles in the body. Despite the diverse appearance and characteristics of organisms on earth, the chemicals that make up living things are remarkably similar, often identical. In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look at the building blocks of the four major classes of biomolecules, how those join up to form macromolecules, and how a. Which three does this video focus on? Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the 4 biological molecules?, what are carbs made of?, what is the simplest form of carbs? In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look at the building blocks of the four major classes of biomolecules, how those join up to form macromolecules, and how a team of six atoms. 1) essential sources of energy, 2) energy storage, 3) instructions to your body why do lipids group together? Valine protects and builds muscle tissue. Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look at the building blocks of the four major classes of biomolecules, how those join up to form macromolecules, and how a team of six atoms. What are the four biological molecules? Biological molecules, and presents the concepts of chemical bonds and reactions. In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look. Despite the diverse appearance and characteristics of organisms on earth, the chemicals that make up living things are remarkably similar, often identical. Valine protects and builds muscle tissue. Tryptophan regulates mood and energy levels. List two specific amino acids and briefly identify their main roles in the body. Click to see the original works with their full license. Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Additional information can be found on this episode’s webpage, including a transcript, references, and. In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look at the building blocks of the four major classes of biomolecules, how those join up to form macromolecules, and how a. We made flashcards to help you review the content in.. In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look at the building blocks of the four major classes of biomolecules, how those join up to form macromolecules, and how a team of six atoms. Living organisms are characterized by several unique. Tryptophan regulates mood and energy levels. List two specific amino acids and briefly identify their main roles in the. Share free summaries, lecture notes, exam prep and more!! Biological molecules, and presents the concepts of chemical bonds and reactions. Valine protects and builds muscle tissue. This material focuses on the critical roles of the four classes of organic molecules essential for life: We made flashcards to help you review the content in. Click to see the original works with their full license. This material focuses on the critical roles of the four classes of organic molecules essential for life: Biological molecules, and presents the concepts of chemical bonds and reactions. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like biological molecules, carbohydrate, lipids and more. Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Tryptophan regulates mood and energy levels. Click to see the original works with their full license. You are what you eat crash course biology #3 1. Additional information can be found on this episode’s webpage, including a transcript, references, and. In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look at the building blocks of the four major classes of biomolecules,. What are the four biological molecules? Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the 4 biological molecules?, what are carbs made of?, what is the simplest form of carbs? In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look at the building blocks of the four major classes of biomolecules, how those join up to form macromolecules,. This material focuses on the critical roles of the four classes of organic molecules essential for life: What are the four biological molecules? Additional information can be found on this episode’s webpage, including a transcript, references, and. 1) essential sources of energy, 2) energy storage, 3) instructions to your body why do lipids group together? Study with quizlet and memorize. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the 4 biological molecules?, what are carbs made of?, what is the simplest form of carbs? Biology is the scientific study of living organisms and their interactions with the environment. We made flashcards to help you review the content in. Living organisms are characterized by several unique. Tryptophan regulates. 1) essential sources of energy, 2) energy storage, 3) instructions to your body why do lipids group together? List two specific amino acids and briefly identify their main roles in the body. Additional information can be found on this episode’s webpage, including a transcript, references, and. Valine protects and builds muscle tissue. What are the four biological molecules? We made flashcards to help you review the content in. Tryptophan regulates mood and energy levels. In this episode of crash course, hank introduces you to the complex history and terminology of anatomy & physiology. This material focuses on the critical roles of the four classes of organic molecules essential for life: Click to see the original works with their full license. You are what you eat crash course biology #3 1. What are the 3 roles that biological molecules play? Biology is the scientific study of living organisms and their interactions with the environment. Despite the diverse appearance and characteristics of organisms on earth, the chemicals that make up living things are remarkably similar, often identical. In this episode of crash course biology, we’ll look at the building blocks of the four major classes of biomolecules, how those join up to form macromolecules, and how a. Living organisms are characterized by several unique.Module A Unit 2 Chemical Basis for Life ppt download
Biological Molecules You Are What You Eat Crash Course Biology
Biomolecules Biological Molecules Introduction Maharashtra SET
Biological Crash Course Molecules Biology crash course Biological
biological molecules you are what you eat_ crash course biology 3
Biological Molecules You Are What You Eat Crash Course Biology 3
Carbon & Biological Molecules What is Life Made Of? Crash Course
Chapter 7 Biomolecules, Lesson 1 Micro And Macro Molecule NEET
Biological Molecules/ Crash Course Biology 5090/ online tutoring YouTube
Crash Course Biology Episode 3 Worksheet Biological Molecules & Nutrition
Which Three Does This Video Focus On?
Share Free Summaries, Lecture Notes, Exam Prep And More!!
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like What Are The 4 Biological Molecules?, What Are Carbs Made Of?, What Is The Simplest Form Of Carbs?
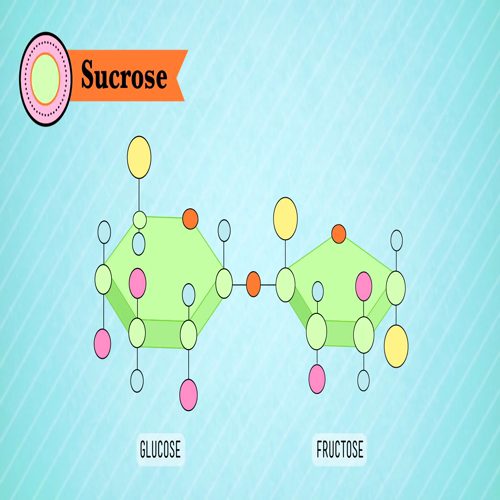
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic Acids, And Lipids.
Related Post: