Holder And Holder In Due Course
Holder And Holder In Due Course - This is the basic difference between the holder and holder in due course. Learn about the holder in due course concept, its rules, examples, and real estate applications. Holder in due course must obtain the instrument in good faith. A holder in due course (hdc) is someone who takes a negotiable instrument without reason to doubt its payment. A holder possesses a negotiable instrument with the right to enforce it, while a holder in due course acquires it in good faith, without defects, and holds superior rights. Holder in due course and privileges: Explore key requirements and legal protections under the ucc. Section 9 of the act defines ‘holder in due course’ as any person who (i) for valuable consideration, (ii) becomes the possessor of a. Learn about the rights, limitations and history of this concept in commercial. Who is a holder in due course? We mean the payee of the negotiable instrument, who is in possession of it. A holder in due course is any person who receives or holds a negotiable instrument such as a check or promissory note in good faith and in exchange for value; Understanding the difference between holder and holder in due course is essential for legal professionals, businesses, and individuals dealing with negotiable instruments to. Learn the meaning and comparison of holder and holder in due course, two terms related to negotiable instruments. Who is a holder in due course? Hence he shall receive or recover the amount due thereon. A holder in due course obtains the negotiable instrument in good faith for consideration prior to it becomes due for payment. Under ucc article 3, a holder in due course is someone who acquires a negotiable instrument in good faith, for value, and without notice of any defects or claims. Learn about the holder in due course concept, its rules, examples, and real estate applications. Explore key requirements and legal protections under the ucc. Who is a holder in due course? Holder in due course must obtain the instrument in good faith. A holder in due course (hdc) is someone who takes a negotiable instrument without reason to doubt its payment. A holder possesses a negotiable instrument with the right to enforce it, while a holder in due course acquires it in good faith,. A holder in due course (hdc) is someone who takes a negotiable instrument without reason to doubt its payment. Holder in due course and privileges: Learn the meaning and comparison of holder and holder in due course, two terms related to negotiable instruments. Holder refers to a person; Explore key requirements and legal protections under the ucc. Hence he shall receive or recover the amount due thereon. We mean the payee of the negotiable instrument, who is in possession of it. Holder in due course and privileges: Explore key requirements and legal protections under the ucc. Holder in due course refers to the. A holder in due course is any person who receives or holds a negotiable instrument such as a check or promissory note in good faith and in exchange for value; Learn the meaning and comparison of holder and holder in due course, two terms related to negotiable instruments. Holder in due course and privileges: Understanding the difference between holder and. Understanding the difference between holder and holder in due course is essential for legal professionals, businesses, and individuals dealing with negotiable instruments to. Holder is a person who is entitled for the possession of a negotiable instrument in his own name. A holder in due course (hdc) is someone who takes a negotiable instrument without reason to doubt its payment.. Holder in due course can be termed as a person who acquires a negotiable instrument for consideration in good faith before it becomes due for payment and without having knowledge. Holder refers to a person; Holder is a person who is entitled for the possession of a negotiable instrument in his own name. This is the basic difference between the. Holder in due course refers to the. Learn the meaning and comparison of holder and holder in due course, two terms related to negotiable instruments. Learn about the holder in due course concept, its rules, examples, and real estate applications. Under ucc article 3, a holder in due course is someone who acquires a negotiable instrument in good faith, for. Learn the meaning and comparison of holder and holder in due course, two terms related to negotiable instruments. We mean the payee of the negotiable instrument, who is in possession of it. Hence he shall receive or recover the amount due thereon. In contrast, a holder in due course, or hdc, refers to someone who acquires the instrument in good. This is the basic difference between the holder and holder in due course. Explore key requirements and legal protections under the ucc. Holder refers to a person; Section 9 of the act defines ‘holder in due course’ as any person who (i) for valuable consideration, (ii) becomes the possessor of a. A holder in due course (hdc) is someone who. Explore key requirements and legal protections under the ucc. Holder refers to a person; A holder possesses a negotiable instrument with the right to enforce it, while a holder in due course acquires it in good faith, without defects, and holds superior rights. We mean the payee of the negotiable instrument, who is in possession of it. A holder in. Learn about the holder in due course concept, its rules, examples, and real estate applications. Learn the meaning and comparison of holder and holder in due course, two terms related to negotiable instruments. Understanding the difference between holder and holder in due course is essential for legal professionals, businesses, and individuals dealing with negotiable instruments to. We mean the payee of the negotiable instrument, who is in possession of it. Hence he shall receive or recover the amount due thereon. Holder in due course and privileges: Holder in due course refers to the. In contrast, a holder in due course, or hdc, refers to someone who acquires the instrument in good faith, for value, and before its maturity date, without knowledge of any defects in the. S/he is someone who is entitled to receive or recover the amount due on the instrument. A holder in due course obtains the negotiable instrument in good faith for consideration prior to it becomes due for payment. Learn about the rights, limitations and history of this concept in commercial. Holder in due course can be termed as a person who acquires a negotiable instrument for consideration in good faith before it becomes due for payment and without having knowledge. Holder is a person who is entitled for the possession of a negotiable instrument in his own name. Section 9 of the act defines ‘holder in due course’ as any person who (i) for valuable consideration, (ii) becomes the possessor of a. Holder refers to a person; Who is a holder in due course?Holder and Holder in Due Course PDF Negotiable Instrument Common Law
Holder and Holder in Due Course PDF Negotiable Instrument Private Law
PPT Negotiable Instruments PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The Negotiable Instruments Act, ppt download
Holder in Due Course
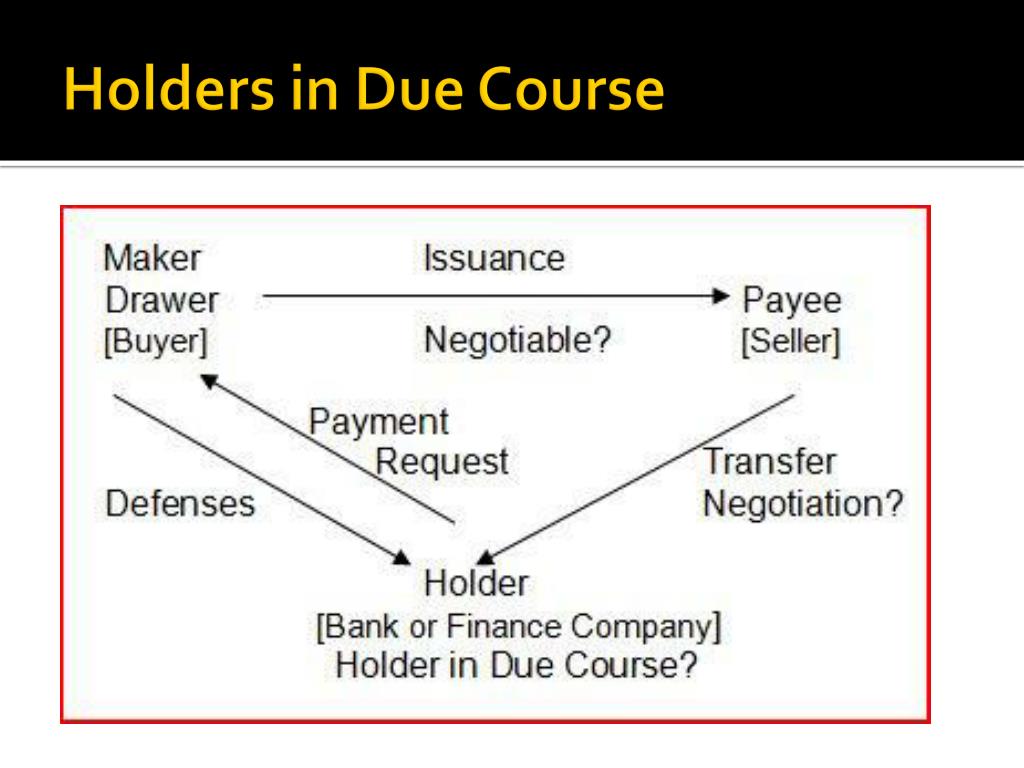
PPT Holders in Due Course PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
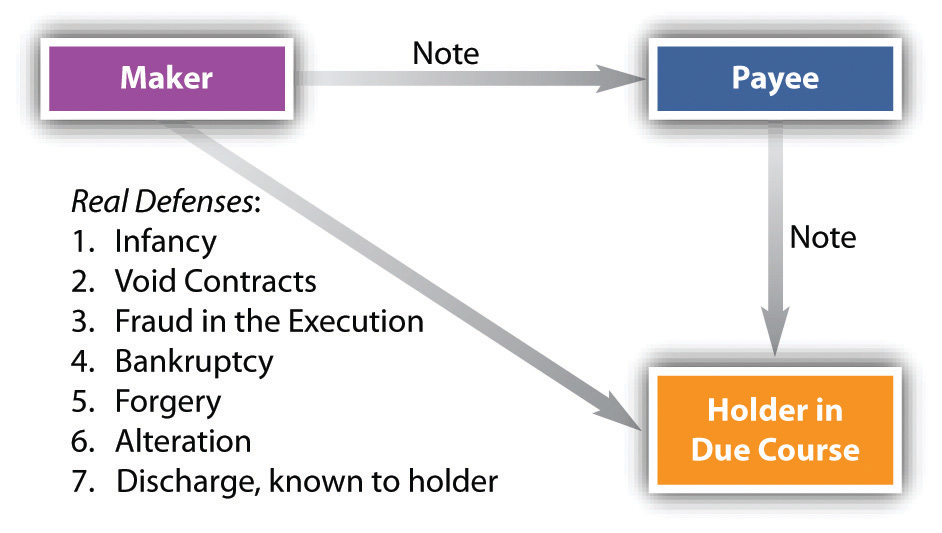
Holder in Due Course and Defenses
Holder and Holder in Due course Dr Manish
PPT Negotiable Instruments PowerPoint Presentation, free download
NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENTS ACT ppt video online download
A Holder In Due Course Is Any Person Who Receives Or Holds A Negotiable Instrument Such As A Check Or Promissory Note In Good Faith And In Exchange For Value;
A Holder In Due Course (Hdc) Is Someone Who Takes A Negotiable Instrument Without Reason To Doubt Its Payment.
A Holder Is A Payee Who Can Sue The Parties Liable, While A Holder In Due Course Is A Bonafide Possessor Who Can Sue All Prior Parties.
This Is The Basic Difference Between The Holder And Holder In Due Course.
Related Post: